KCL is a constraint-based record and functional language hosted by Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) that enhances the writing of complex configurations, including those for cloud-native scenarios. With its advanced programming language technology and practices, KCL is dedicated to promoting better modularity, scalability, and stability for configurations. It enables simpler logic writing and offers ease of automation APIs and integration with homegrown systems.
This section will update the KCL language community's latest developments every two weeks, including features, website updates, and the latest community news, helping everyone better understand the KCL community!
KCL Website: https://kcl-lang.io
Overview
Thanks to to all contributors for their outstanding work over the past two weeks (01.19 2024 - 02.01 2024). Here is an overview of the key content:
📦 Module Updates
- Added the
podinfoapplication configuration module, supporting the setting of external dynamic parameters such asreplicas. You can directly render Kubernetes manifests with a single command, and customize KCL templates based on this module.
kcl run oci://ghcr.io/kcl-lang/podinfo -D replicas=2
🏄 Language Updates
- Improved error messages when object attribute are not found at compile time.
- Fixed the recursive check error for mandatory attribute of schema objects.
- Enhanced the robustness of type-checking for schema index signatures.
🔧 Toolchain Updates
- Documentation Tools Updates: Added support for HTML escaping of multiline strings in generated Markdown documentation.
- CodeQL KCL Tools: Preliminary support for the CodeQL KCL dbschema definition and data extraction from KCL syntax and semantics, enabling static analysis and scanning of KCL code through CodeQL queries to improve code security.
💻 IDE Updates
Semantic Highlighting
- KCL IDE optimized semantic highlighting.
Enhancement for Completion Features
- Fixed the issue with erroneous completions after strings followed by comments.
- Fixed the issue where internal property symbols in Schema could not be navigated.
🎁 API Updates
- Added syntax and semantic analysis APIs for analyzing KCL code.
- Added APIs to build binary artifacts for caching compilation results.
- Added APIs to run binary artifacts directly, avoiding recompilation and improving performance.
- Added code generation APIs to programmatically implement KCL code generation instead of writing complex templates.
🚀 SDK Updates
- Updated KCL Go SDK to version 0.7.5.
- Updated KCL Python SDK to version 0.7.5.
- Updated KCL Rust SDK to version 0.7.5.
- Added definitions for syntax trees, scopes, symbols, and other syntactic and semantic structures to the KCL Java SDK, along with related query APIs.
For more details, visit: https://github.com/kcl-lang/lib
🚢 Integration Updates
- In addition to the ArgoCD KCL plugin, KCL now supports GitOps for KCL configurations stored in Git/OCI repositories using the KCL Flux Controller. For more details, visit https://github.com/kcl-lang/flux-kcl-controller. Contributions are welcome 👏.
Special Thanks
The following are listed in no particular order:
- Thanks to @octonawish-akcodes for contributions to KCL code cleanup and FAQ documents. 🙌
- Thanks to @satyazzz123 for contributions to the KRM KCL's support for reading environment variables. 🙌
- Thanks to @AkashKumar7902 for contributions to the KCL package management tool functionality. 🙌
- Thanks to @UtkarshUmre for contributions to the KCL linux-arm64 build CI scripts. 🙌
- Thanks to @steeling, @rozaliev, @CloudZero357, @martingreber, @az, @Art3mK, @AdmiralNemo, and @Erick for valuable suggestions and feedback during the past two weeks of using KCL. 🙌
Featured Updates
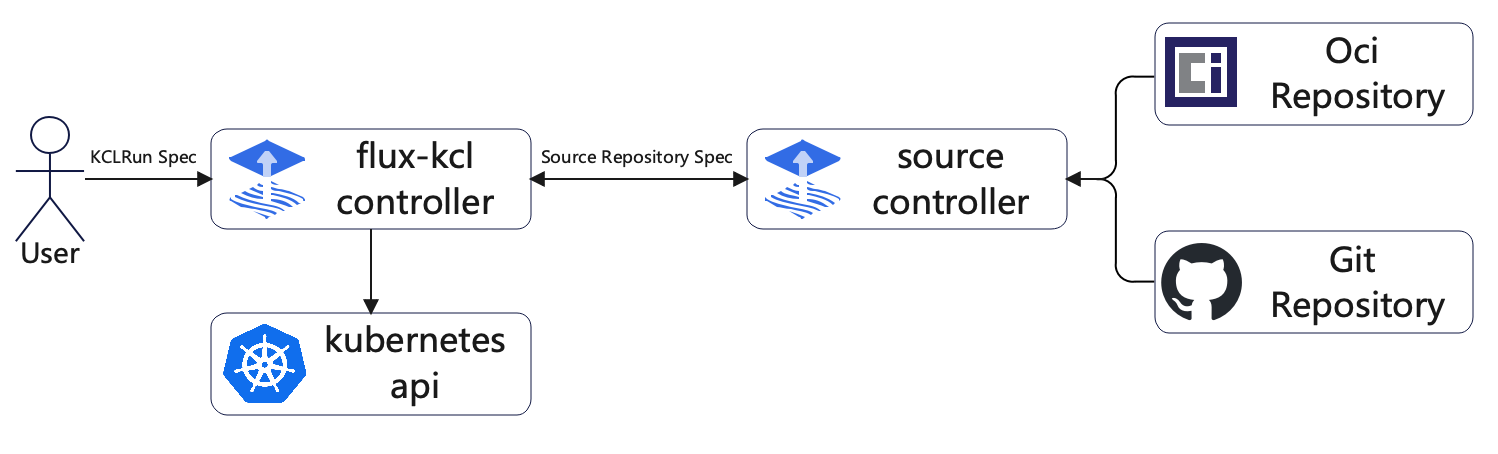
Flux KCL Integration
Using KCL together with GitOps tools like Flux has the following benefits:
- The abstraction and programmability capabilities of KCL can help simplify complex Kubernetes deployment configurations, reducing the error rate of manually writing YAML files. It allows for configuration constraint checks at compile-time, making it easier to detect errors. Additionally, it eliminates redundant configuration templates, improves the scalability of configurations across multiple environments and tenants, and enhances configurability and maintainability.
- KCL allows developers to define the required resources for an application in a declarative manner. Combining KCL with Flux enables better implementation of Infrastructure as Code (IaC), improving deployment efficiency and simplifying application configuration management.
- With Flux, developers and operations teams can manage the deployment of applications by separately modifying application and configuration code. The Flux Controller automatically synchronizes changes to the configuration, enabling continuous deployment and ensuring consistency. In case of issues, quick rollbacks can be achieved.
Workflow
In this example, we use a Python Flask application and GitHub Actions as a CI example. The Flux KCL Controller is deployed in the cluster as a CD example. KCL is used to define the Kubernetes resources that need to be deployed.
Note: You can use any containerized application and different CI/CD systems like GitLab CI, Jenkins CI, or ArgoCD in this scenario.
We divide the Python Flask application code and configuration code into two repositories to separate the concerns of different roles such as developers and operations teams.
- Business code repository: https://github.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo
- Manifests repository: https://github.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo-kcl-manifests
The overall workflow is as follows:
- Pull the application code from GitHub.
- Develop the application code and commit it to the GitHub repository.
- Trigger GitHub Actions to compile the application code, generate a container image, and push the container image to the Docker Hub container registry.
- Trigger GitHub Actions to update the Kubernetes manifest deployment files defined by KCL based on the version of the container image in the docker.io container registry.
- The Flux KCL Controller retrieves the changes to the Kubernetes manifest defined by KCL and updates the deployment to the Kubernetes cluster.
Specific Steps
1. Prepare a Kubernetes Cluster
- Install K3d and create a cluster:
k3d cluster create
Note: You can use other methods to create your own Kubernetes cluster, such as kind, minikube, etc.
- Install kubectl
- Install kustomize
2. Install Flux KCL Controller
git clone https://github.com/kcl-lang/flux-kcl-controller.git && cd flux-kcl-controller && make deploy
3. Configure the Git Repository for Continuous Delivery
Define the GitRepository and KCLRun objects in the gitrepo.yaml file to configure the Git repository to be monitored for continuous delivery and additional parameters required for running KCL configurations.
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: kcl-deployment
namespace: default
spec:
interval: 10s # Check the repository every 10s
url: https://github.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo-kcl-manifests.git
ref:
branch: main # Monitor the main branch
---
apiVersion: krm.kcl.dev.fluxcd/v1alpha1
kind: KCLRun
metadata:
name: kcl-git-controller
namespace: default
spec:
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: kcl-deployment
Deploy the objects to the cluster using the command kubectl apply -f gitrepo.yaml.
If you are using a private repository, you need to configure private repository access credentials using private key credentials. Refer to here for more details.
Note: You can also use OCIRepository in this scenario to continuously deliver the
oci://ghcr.io/kcl-lang/podinfoconfiguration package mentioned at the beginning of the article. For example, the following configuration:
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2
kind: OCIRepository
metadata:
name: podinfo
namespace: default
spec:
interval: 5m0s
url: oci://ghcr.io/kcl-lang/podinfo
ref:
tag: latest
---
apiVersion: krm.kcl.dev.fluxcd/v1alpha1
kind: KCLRun
metadata:
name: kcl-git-controller
namespace: default
spec:
sourceRef:
kind: OCIRepository
name: podinfo
4. Commit the Application Code
After submitting in the flask-demo repository, Github will automatically build a container image and push it to the Docker hub. It will also then trigger the Action of the flask-demo-kcl-manifest repository and modify the image value in the deployment manifest repository through KCL Automation API. Now let's create a submission in the flask-demo repository, and we can see that the code submission triggers the Github CI process for the application repository.
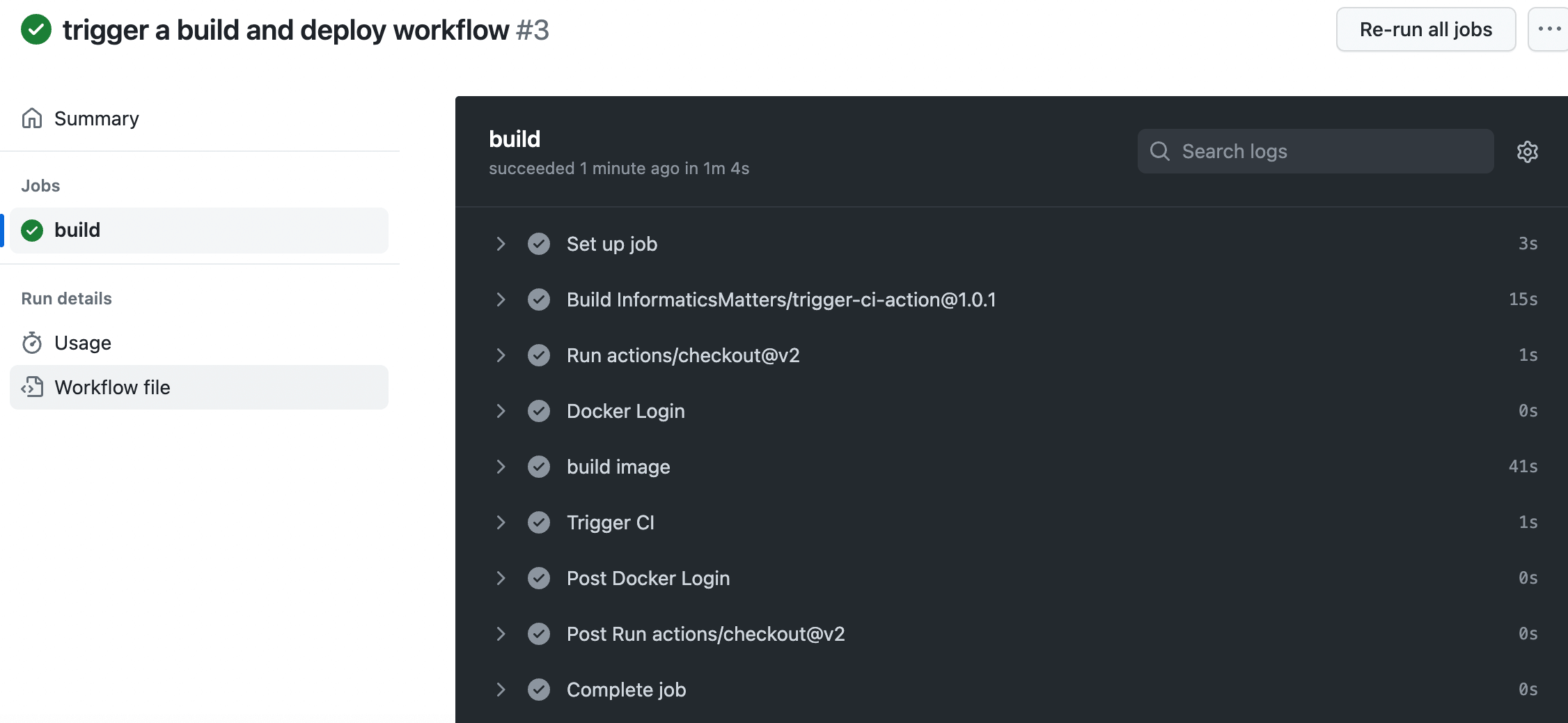
5. Configuration Automatic Update
After the Github CI process in the application repository is completed, an automatic update configuration CI will be triggered in the repository where the KCL configuration is stored and submitted to the main branch of the flask-demo-kcl-manifests repository. The commit information is as follows
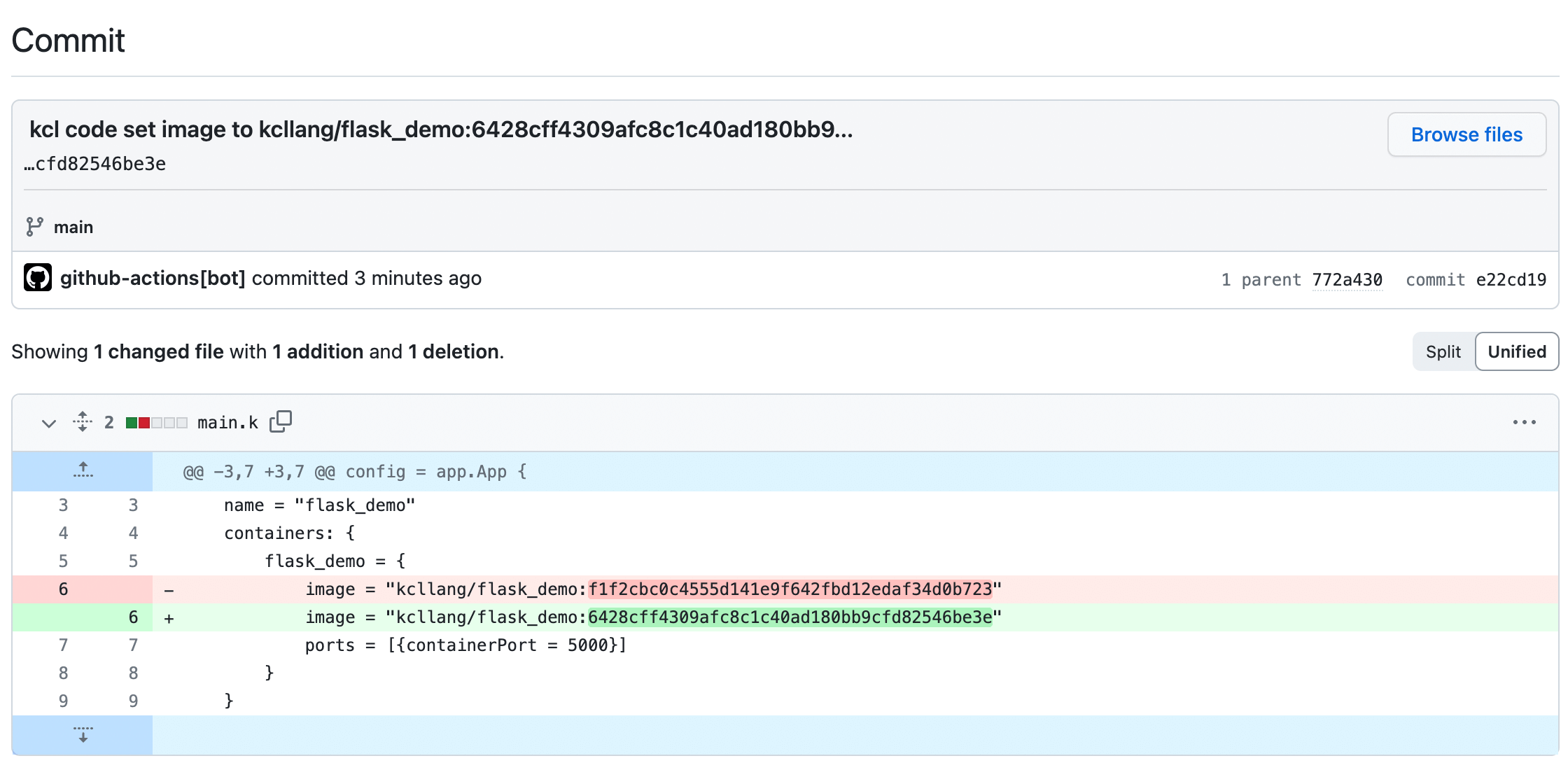
- We can obtain the deployment manifest source code for compilation and validation
git clone https://github.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo-kcl-manifests.git/
cd flask-demo-kcl-manifests
git checkout main && git pull && kcl
The output YAML is
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: flask_demo
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flask_demo
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
containers:
- name: flask_demo
image: "kcllang/flask_demo:6428cff4309afc8c1c40ad180bb9cfd82546be3e"
ports:
- protocol: TCP
containerPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask_demo
labels:
app: flask_demo
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: flask_demo
ports:
- port: 5000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5000
From the above configuration, it can be seen that the image of the resource is indeed automatically updated to the newly constructed image value.
At the same time, the Flux KCL Controller will automatically pull the configuration and update it to the cluster. This achieves an end-to-end automation process for submitting business code and deploying Kubernetes, where only the business code needs to be submitted. Of course, it can be further combined with Flagger to implement various deployment strategies such as canary releases, blue-green deployments, etc.
Resources
❤️ Thanks to all KCL users and community members for their valuable feedback and suggestions in the community. See here to join us!
For more resources, please refer to