
KCL is a constraint-based record and functional language hosted by Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) that enhances the writing of complex configurations, including those for cloud-native scenarios. With its advanced programming language technology and practices, KCL is dedicated to promoting better modularity, scalability, and stability for configurations. It enables simpler logic writing and offers ease of automation APIs and integration with homegrown systems.
This section will update the KCL language community's latest developments every two weeks, including features, website updates, and the latest community news, helping everyone better understand the KCL community!
KCL Website: https://kcl-lang.io
Overview
Thank you to all contributors for their outstanding work over the past two weeks (11.24 - 12.07 2023). Here is an overview of the key content:
📦 Model Updates
KCL model quantity increased to 300, added KCL models for k8s 1.29.
🔧 Toolchain Updates
Import Tool Updates
- Import tool supports OpenAPI allOf keyword validation expression generation
- Import tool supports KCL array and dictionary type all/any validation expression generation
- Import tool fixes JSON Schema array generation KCL code snippet error and string escape error
🏄 Package Management Tool Updates
- Added support for third-party libraries with hyphens in their names.
- Fixed the problem that the update function cannot automatically pass kcl.mod and kcl.mod.lock.
💻 KCL Updates
- KCL compilation cache path supports using environment variables KCL_CACHE_PATH to specify
- Fixed the compilation error that may be caused by the compilation parameter -S of KCL CLI
- Fixed the error that kcl fmt tool adds an empty line at the end when formatting lambda expressions.
- Fixed Schema Doc completion code snippet error
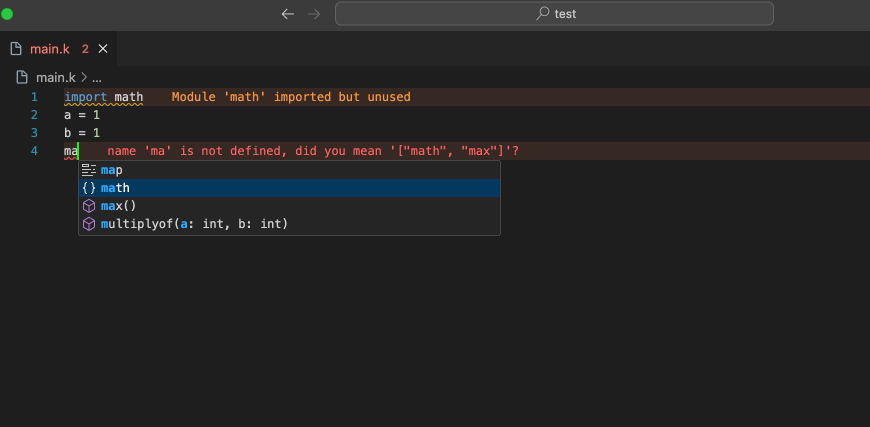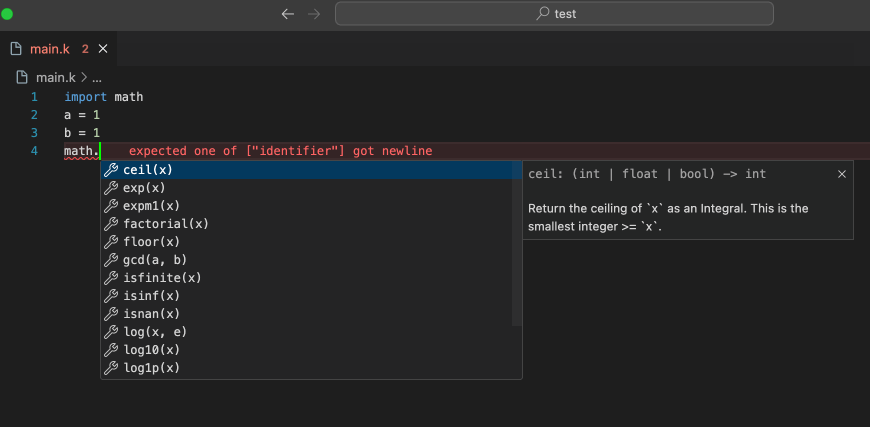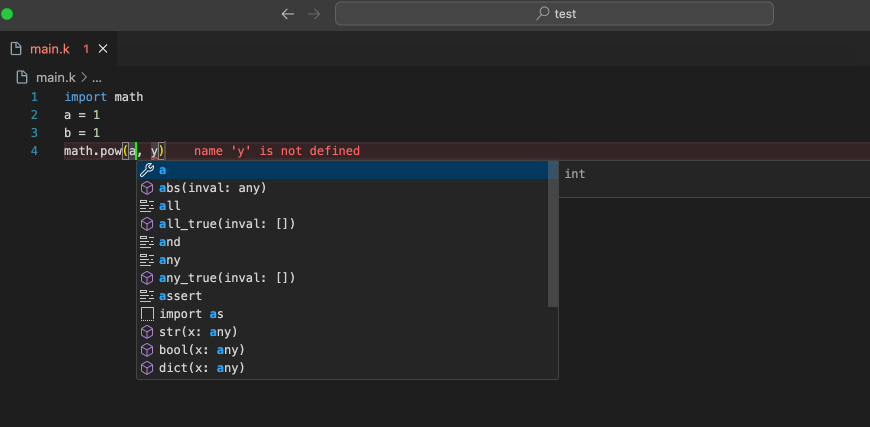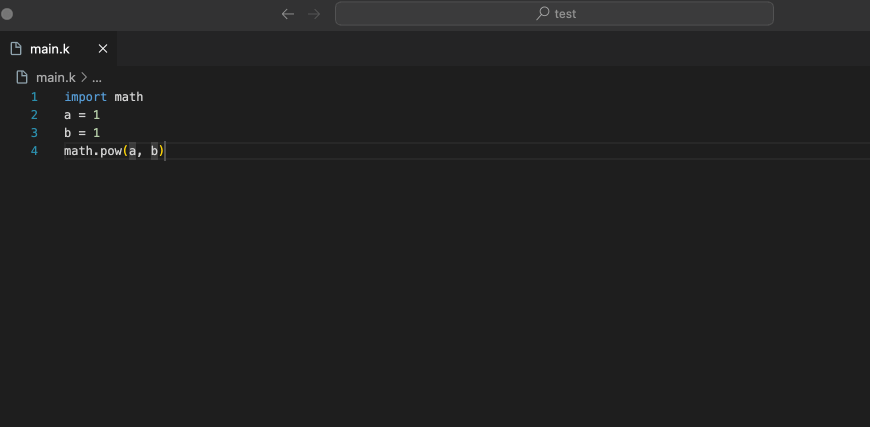
📒 IDE Updates
- Fixed the problem that the variable completion in the check statement is invalid
- VSCode Extension updated to version 0.1.3, updated the highlighting and completion of some keywords
- Added completion of builtin functions
- Optimized the style of function completion
Featured Updates
Efficient Cloud Native Application Deployment - KCL and KubeVela Integration Quick Guide
KCL is a configuration and policy language for cloud-native scenarios, hosted by the CNCF Foundation. It aims to improve the writing of complex configurations, such as cloud-native Kubernetes configurations, using mature programming language techniques and practices. KCL focuses on building better modularity, scalability, and stability around configuration, as well as easier logic writing, automation, and integration with the toolchain.
KCL exists in a completely open cloud-native world and is not tied to any orchestration/engine tools or Kubernetes controllers. It can provide API abstraction, composition, and validation capabilities for both Kubernetes clients and runtime.
KubeVela is a modern application delivery system hosted by the CNCF Foundation. It is built on the Open Application Model (OAM) specification and aims to abstract the complexity of Kubernetes, providing a set of simple and easy-to-use command-line tools and APIs for developers to deploy and operate cloud-native applications without worrying about the underlying details.
Using KCL with KubeVela has the following benefits:
- Simpler configuration: KCL provides stronger templating capabilities, such as conditions and loops, for KubeVela OAM configurations at the client level, reducing the need for repetitive YAML writing. At the same time, the reuse of KCL model libraries and toolchains enhances the experience and management efficiency of configuration and policy writing.
- Better maintainability: KCL provides a configuration file structure that is more conducive to version control and team collaboration, instead of relying solely on YAML. When combined with OAM application models written in KCL, application configurations become easier to maintain and iterate.
- Simplified operations: By combining the simplicity of KCL configurations with the ease of use of KubeVela, daily operational tasks such as deploying, updating, scaling, or rolling back applications can be simplified. Developers can focus more on the applications themselves rather than the tedious details of the deployment process.
- Improved cross-team collaboration: By using KCL's configuration chunk writing and package management capabilities in conjunction with KubeVela, clearer boundaries can be defined, allowing different teams (such as development, testing, and operations teams) to collaborate systematically. Each team can focus on tasks within their scope of responsibility, delivering, sharing, and reusing their own configurations without worrying about other aspects.
Taking the KCL Playground application (written in Go and HTML5) as an example, we use KCL to define the OAM configuration that needs to be deployed. The overall workflow is as follows:
Prepare
- Configure the Kubernetes cluster
- Install KubeVela
- Install KCL
New project and add OAM dependency
kcl mod init kcl-play-svc && cd kcl-play-svc && kcl mod add oam
- Write code in main.k
import oam
oam.Application {
metadata.name = "kcl-play-svc"
spec.components = [{
name = metadata.name
type = "webservice"
properties = {
image = "kcllang/kcl:v0.9.0"
ports = [{port = 80, expose = True}]
cmd = ["kcl", "play"]
}
}]
}
- Run command to deploy configuration
kcl run | vela up -f -
- Port forwarding
vela port-forward kcl-play-svc
Then we can see the KCL Playground application running successfully in the browser
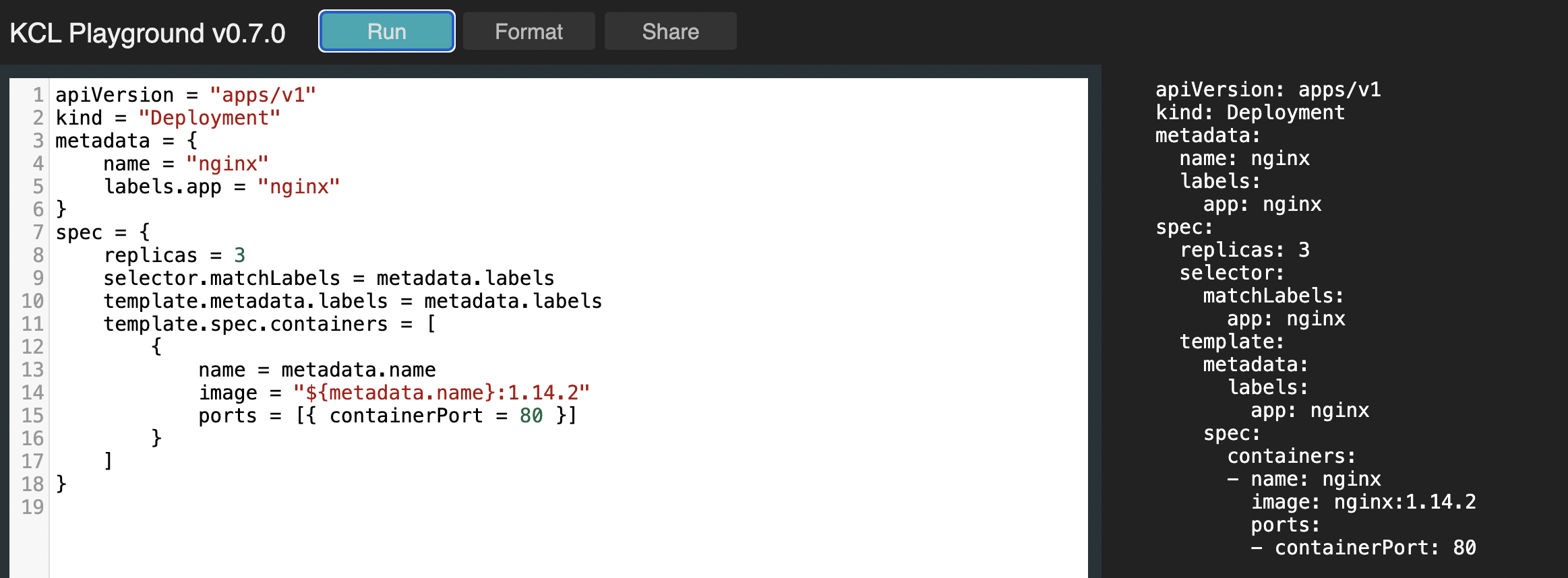
IDE Optimized the Style of Function Completion
Resources
❤️ Thanks to all KCL users and community members for their valuable feedback and suggestions in the community. See here to join us!
For more resources, please refer to