Automation
Introduction
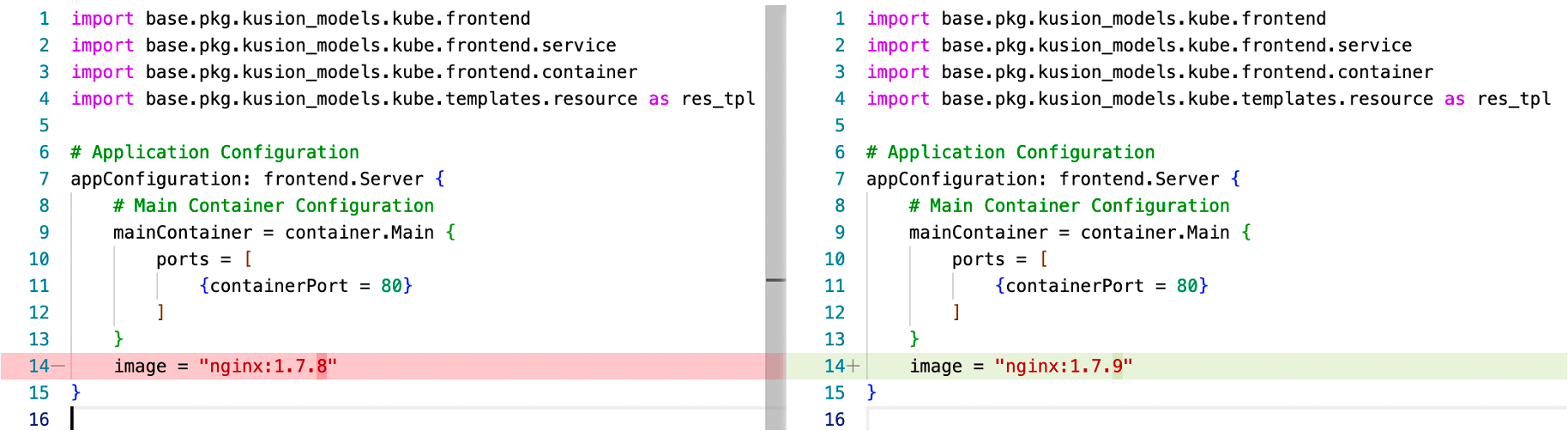
KCL provides many automation related capabilities, mainly including tools and multilingual APIs. Via package_identifier : key_identifier mode, KCL supports the indexing of any configured key value, thus completing the addition, deletion, modification and query of any key value. For example, the following figure shows that we can directly execute the following command to modify the image. The code diff before and after modification is also shown in the figure.
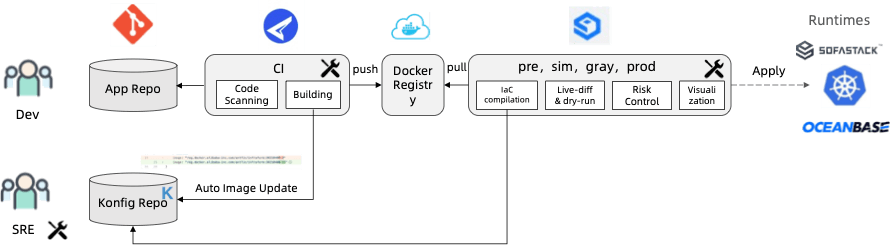
In addition, the automation capability of KCL can be realized and integrated into CI/CD.
Use KCL for Automation
0. Prerequisite
- Install KCL
1. Get the Example
Firstly, let's get the example.
git clone https://github.com/kcl-lang/kcl-lang.io.git/
cd ./kcl-lang.io/examples/automation
We can run the following command to show the config.
cat main.k
The output is
schema App:
"""The application model."""
name: str
replicas: int
labels?: {str:str} = {app = name}
app: App {
name = "app"
replicas = 1
labels.key = "value"
}
We can run the command to get the config
kcl main.k
The output is
app:
name: app
replicas: 1
labels:
app: app
key: value
2. Use KCL CLI for Automation
KCL allows us to directly modify the values in the configuration model through the KCL CLI -O|--overrides parameter. The parameter contains three parts e.g., pkg, identifier, attribute and override_value.
kcl main.k -O override_spec
override_specrepresents a unified representation of the configuration model fields and values that need to be modified
override_spec: identifier (("=" | ":" | "+=") value | "-")
identifierindicates the identifier that needs to modify the configuration, usually in the form ofa.b.cora["dot.key"].cvalueindicates the value of the configuration that needs to be modified, which can be any legal KCL expression, such as number/string literal value, list/dict/schema expression, etc.=,:and+=denotes modifying of the value of the identifier with the corresponding attribute operator.- When the identifier exists, modify the value of the existing identifier to value.
- When identifier does not exist, add the identifier attribute and set its value to value.
-denotes deleting of the identifier.- When the identifier exists, delete it directly.
- When the identifier does not exist, no modification is made to the configuration.
Override Configuration
Run the command to update the application name.
kcl main.k -O app.name=\'new_app\'
The output is
app:
name: new_app
replicas: 1
labels:
app: new_app
key: value
We can see the name attribute of the app config is updated to new_app.
Besides, when we use KCL CLI -d argument, the KCL file will be modified to the following content at the same time.
kcl main.k -O app.name=\'new_app\' -d
schema App:
"""The application model."""
name: str
replicas: int
labels?: {str:str} = {app = name}
app: App {
name = "new_app"
replicas = 1
labels: {key = "value"}
}
Note that when name of app is not in the App schema config, it will be added into the config after override.
Delete Configuration
Run the command to delete the key attribute of labels.
kcl main.k -O app.labels.key-
The output is
app:
name: app
replicas: 1
labels:
app: app
3. Use KCL API for Automation
In addition, we can automatically modify the configuration attributes through the multilingual API.
Take the RestAPI as an example. The RestAPI service can be started in the following way:
kcl server
The service can then be requested via the POST protocol:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:2021/api:protorpc/KclvmService.OverrideFile -H 'content-type: accept/json' -d '{
"file": "main.k",
"specs": ["app.name=\"nginx\""]
}'
After the service call is completed, main.k will be modified as follows:
schema App:
"""The application model."""
name: str
replicas: int
labels?: {str:str} = {app = name}
app: App {
name = "nginx"
replicas = 1
labels: {
"key" = "value"
}
}
Summary
The document introduces the automation capabilities of KCL, including tools and multilingual APIs. It supports indexing of any configured key value, allowing for the addition, deletion, modification, and querying of any key value. It can also be integrated into CI/CD. The document provides an example of using KCL to automate configuration management, including using the KCL CLI to override and delete configurations, and using the KCL API to modify configuration attributes. For more information about KCL automation and Override API, please refer to here.