Quick Start
Introduction
What is GitOps
GitOps is a modern way to do continuous delivery. Its core idea is to have a Git repository which contains environmental and application configurations. An automated process is also needed for sync the config to cluster.
By changing the files in repository, developers can apply the applications automatically. The benefits of applying GitOps include:
- Increased productivity. Continuous delivery can speed up the time of deployment.
- Lower the barrier for developer to deploy. By pushing code instead of container configuration, developers can easily deploy Kubernetes without knowing its internal implementation.
- Trace the change records. Managing the cluster with Git makes every change traceable, enhancing the audit trail.
- Recover the cluster with Git's rollback and branch.
GitOps with KCL
Benefits of Using KCL and ArgoCD Together:
- KCL can help us simplify complex Kubernetes deployment configuration files, reduce the error rate of manually writing YAML files, and improve code readability and maintainability.
- ArgoCD can automate the deployment of Kubernetes applications, achieve continuous deployment, and provide comprehensive monitoring and control functions.
- By combining KCL and ArgoCD, deployment efficiency can be improved, errors reduced, and management and monitoring of Kubernetes applications strengthened.
- The combination of KCL and ArgoCD can also help us achieve Infrastructure as Code (IaC), simplify application deployment and management, and better implement DevOps principles.
With GitOps, developer and operation teams can manage application deployment and configuration by modifying KCL code and generating YAML files. The GitOps toolchain will automatically synchronize the changes to the Kubernetes cluster, enabling continuous deployment and ensuring consistency. If there are issues, the GitOps toolchain can be used to quickly rollback.
Prerequisite
- Install KCL
How to
1. Get the Example
Firstly, let's get the example.
git clone https://github.com/kcl-lang/kcl-lang.io.git/
cd ./kcl-lang.io/examples/gitops
We can run the following command to show the config.
cat config/main.k
The output is
import .app
config = app.App {
name = "kcl-guestbook-ui"
containers.guestbook = {
image = "gcr.io/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo:0.2"
ports = [{containerPort = 80}]
}
service.ports = [{ port = 80 }]
service.type = "LoadBalancer"
}
In the above code, we defined a configuration using the App schema, where we configured an gcr.io/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo:0.2 container and configured it with an 80 service port.
2. Install Kubernetes and GitOps Tool
Setup Kubernetes Cluster and ArgoCD Controllers
- Install K3d to create a default cluster.
k3d cluster create mycluster
- Install ArgoCD.
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
- Enable ArgoCD KCL Plugin
Write the patch YAML configuration file and update the ArgoCD configuration:
kubectl apply -f ./install/kcl-cmp.yaml
After completing the first step, ArgoCD will recognize the KCL plugin, but the KCL plugin has not been loaded into the ArgoCD image. To implement configuration drift detection, we have to tune the Deployment of argocd-repo-server.
kubectl -n argocd patch deploy/argocd-repo-server -p "$(cat ./install/patch-argocd-repo-server.yaml)"
Wait for the init container to complete execution (Running).
kubectl get pod -n argocd -l app.kubernetes.io/name=argocd-repo-server
- To access the ArgoCD web UI
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
Open a browser and go to:
https://localhost:8080The username is "admin" and password get be obtained from the following command:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
Setup ArgoCD CLI
- Install ArgoCD CLI
Use "admin" and password to login to ArgoCD
argocd login localhost:8080
Create ArgoCD Application
argocd app create guestbook \
--repo https://github.com/kcl-lang/kcl-lang.io \
--path examples/gitops/config \
--dest-namespace default \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--config-management-plugin kcl-v1.0
If you are using a private repository, you need to configure the private repository access with private key credentials before executing the create command.
Please refer Private Repositories for more details.
After successfully creating, you can see the following output:
application 'guestbook' created
Through the ArgoCD UI, you can see that the created applications have not been synchronized yet. Here, you can manually synchronize or set automatic synchronization.
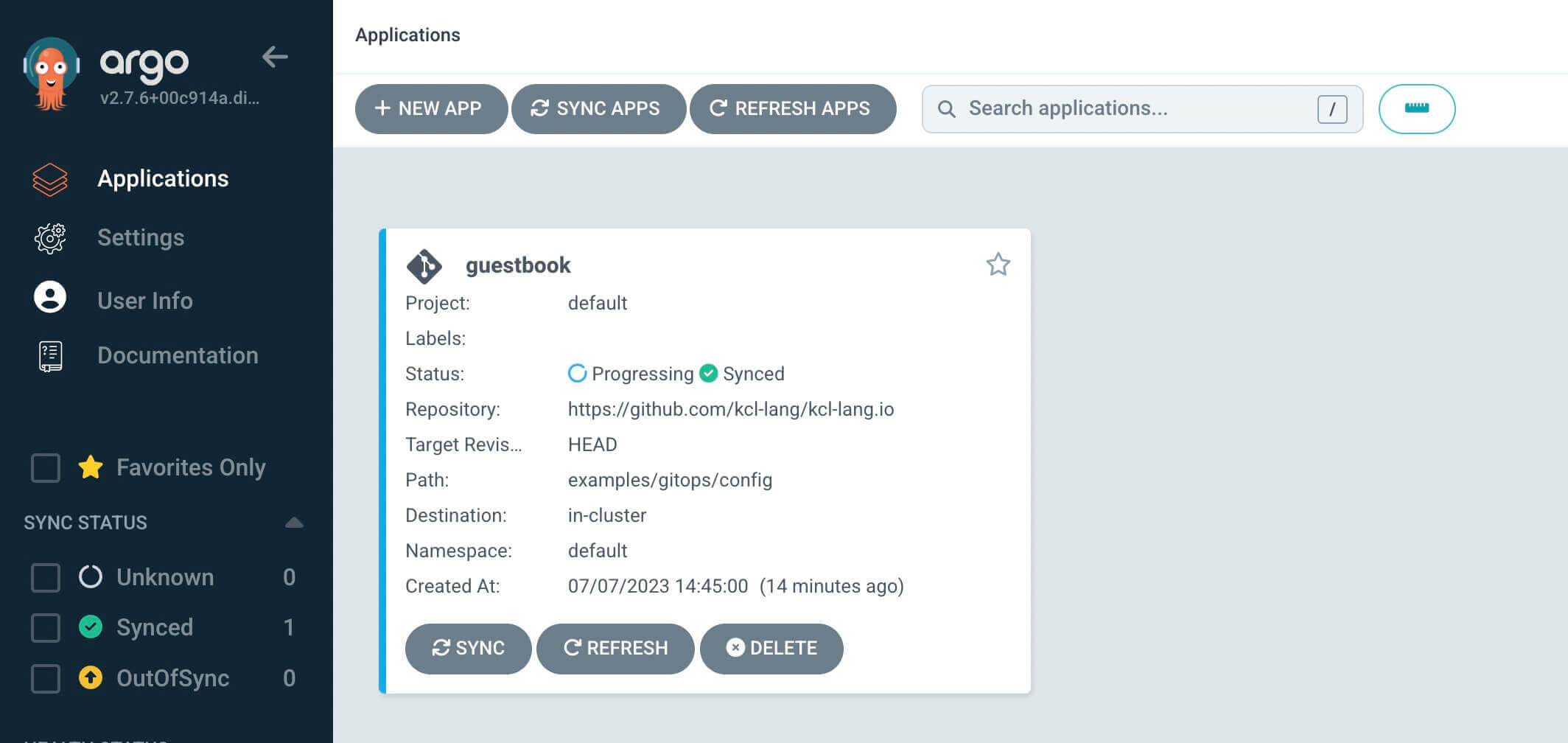
For more information on synchronization strategies, see Sync Options
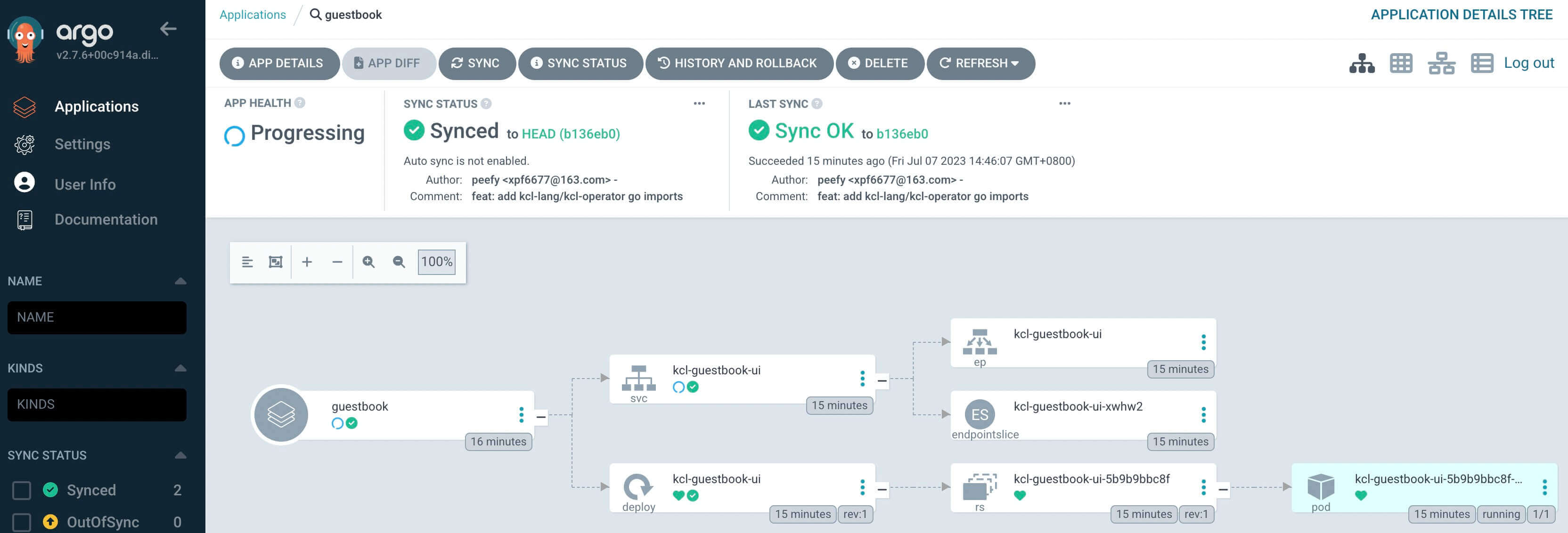
Summary
With GitOps, you can easily manage your applications and configuration in your Kubernetes cluster with KCL, ensuring that your applications are always in the desired state.