Quick Start
Introduction
What is GitOps
GitOps is a modern way to do continuous delivery. Its core idea is to have a Git repository which contains environmental and application configurations. An automated process is also needed for sync the config to cluster.
By changing the files in repository, developers can apply the applications automatically. The benefits of applying GitOps include:
- Increased productivity. Continuous delivery can speed up the time of deployment.
- Lower the barrier for developer to deploy. By pushing code instead of container configuration, developers can easily deploy Kubernetes without knowing its internal implementation.
- Trace the change records. Managing the cluster with Git makes every change traceable, enhancing the audit trail.
- Recover the cluster with Git's rollback and branch.
GitOps with KCL and FluxCD
Benefits of Using KCL and FluxCD Together:
- KCL can help us simplify complex Kubernetes deployment configuration files, reduce the error rate of manually writing YAML files, and improve code readability and maintainability.
- FluxCD can automate the deployment of Kubernetes applications, achieve continuous deployment, and provide comprehensive monitoring and control functions.
- By combining KCL and FluxCD, deployment efficiency can be improved, errors reduced, and management and monitoring of Kubernetes applications strengthened.
- The combination of KCL and FluxCD can also help us achieve Infrastructure as Code (IaC), simplify application deployment and management, and better implement DevOps principles.
With GitOps, developer and operation teams can manage application deployment and configuration by modifying KCL code and generating YAML files. The GitOps toolchain will automatically synchronize the changes to the Kubernetes cluster, enabling continuous deployment and ensuring consistency. If there are issues, the GitOps toolchain can be used to quickly rollback.
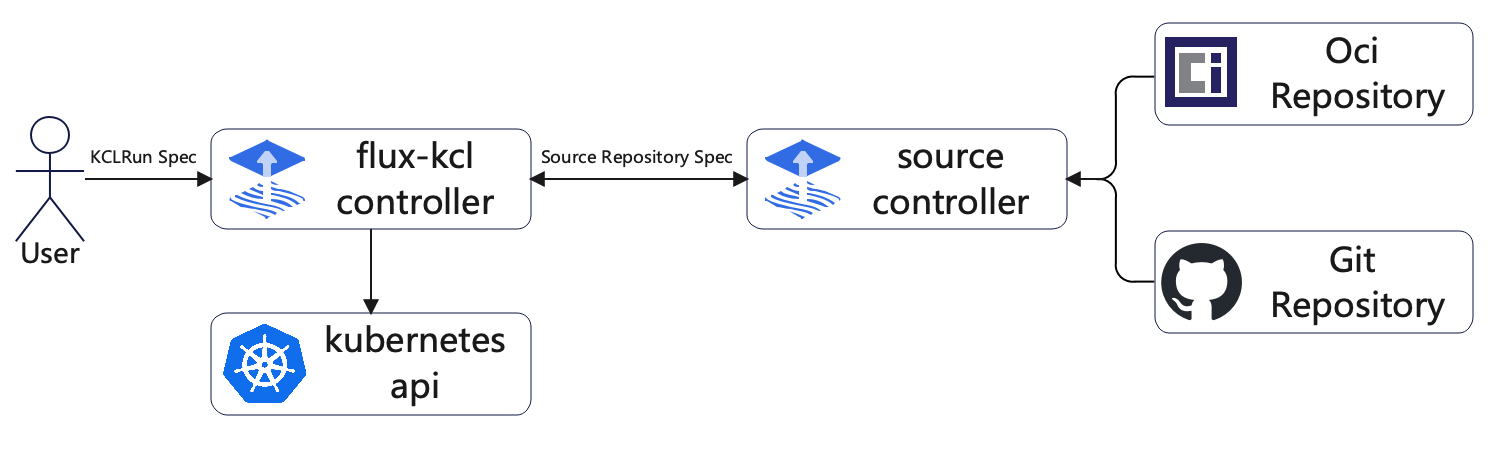
Flux-KCL-Controller
flux-kcl-controller is a component that integrates KCL and Flux, which is mainly used to define infrastructure and workloads based on KCL programs stored in git/oci repositories, and to achieve continuous delivery of infrastructure and workloads through [source-controller](
Prerequisite
- Install KCL
Quick Start
1. Install Kubernetes and GitOps Tools
Configure Kubernetes Cluster and FluxCD Controller
- Install K3d to create a default cluster.
k3d cluster create mycluster
- Install Flux KCL Controller
git clone https://github.com/kcl-lang/flux-kcl-controller.git && cd flux-kcl-controller && make deploy
- Check if the fluxcd controller container is initialized and running by using the
kubectl getcommand.
kubectl get pod -n source-system -l app=kcl-controller
2. Write Flux-KCL-Controller Configuration File
Create a GitRepository object for flux-kcl-controller to monitor the KCL program stored in the git repository. For example, we use the flask demo in “Implementing GitOps using Github, Argo CD, and KCL to Simplify DevOps” as an example. We create a GitRepository object in the flux-kcl-controller repository to monitor the KCL program stored in the git repository. Save the following content in the file gitrepo.yaml.
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: kcl-deployment
namespace: default
spec:
interval: 10s # Check every 10 seconds
url: https://github.com/kcl-lang/flask-demo-kcl-manifests.git
ref:
branch: main # Monitor the main branch
---
apiVersion: krm.kcl.dev.fluxcd/v1alpha1
kind: KCLRun
metadata:
name: kcl-git-controller
namespace: default
spec:
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: kcl-deployment
Apply the GitRepository object to the cluster by running the kubectl apply -f gitrepo.yaml command.
3. Check the Deployment Result
Check the deployment result by running the kubectl get deployments command.
kubectl get deployments
You can see the result, and the deployment is successful.
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
flask-demo 1/1 1 1 17d